GitHub Code Quality is now in public preview, and it’s built around a simple premise: catch maintainability and reliability issues when they’re easiest to fix — during the pull request, not six months later when you’re deep in a production incident.
What it does#
The feature surfaces CodeQL-powered quality checks directly in your pull requests, covering Java, C#, Python, JavaScript, Go, and Ruby. You see issues inline with context, and Copilot can fix many of them with a single click.
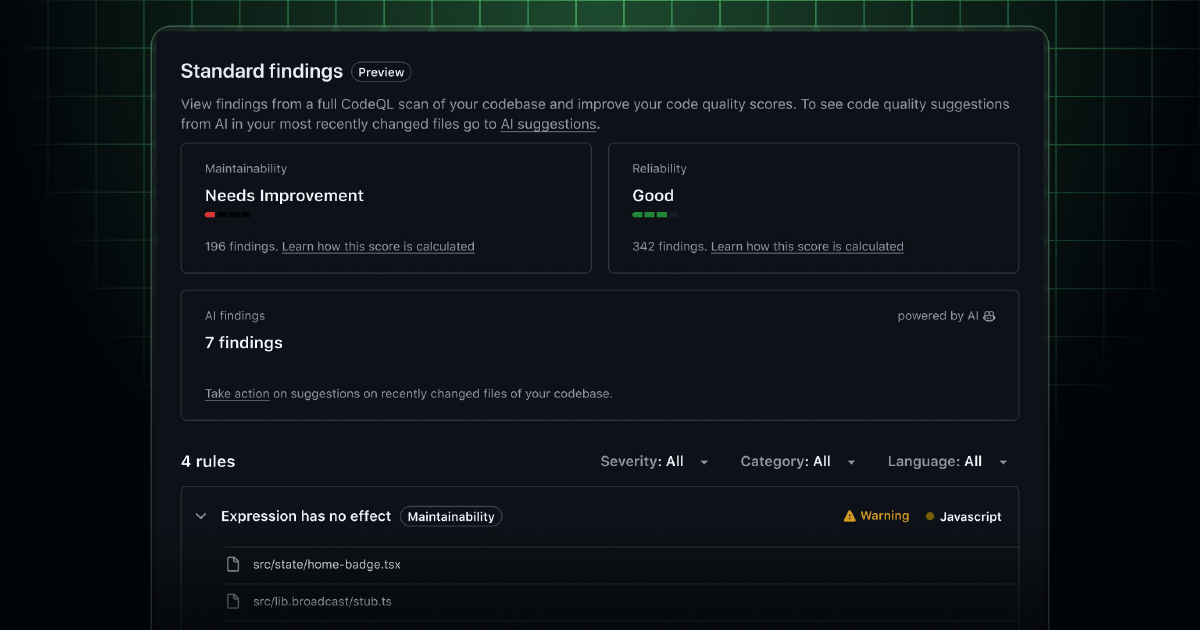
The quality repository view groups findings by rule and provides reliability and maintainability scores. That scoring turns an overwhelming backlog of technical debt into something you can prioritize.
Why timing matters#
Here’s the interesting part: code review is when developers are already thinking about whether the code is good enough to merge. Adding quality feedback at that exact moment is natural — it’s part of the conversation you’re already having.
Compare that to a separate static analysis tool that emails you warnings later. By then, context is gone. The engineer has moved on. Fixing it feels like rework instead of refinement.
GitHub is embedding quality checks into the pull request flow, which means quality becomes part of the definition of “done,” not something you address if you have time.
Copilot autofixes#
The one-click fix is the feature that matters most here. Static analysis tools have always had a problem: they’re great at finding issues but terrible at making it easy to fix them.
If Copilot can autofix the majority of quality issues inline during review, then the cost of addressing quality drops dramatically. It’s the difference between “this needs work” and “click here to fix it.”
The question is what percentage of findings are actually autofixable, and whether those fixes are correct enough to trust without manual verification. GitHub hasn’t published those numbers yet.
Technical debt becomes visible#
The quality scores — reliability and maintainability — give you a way to measure what’s usually subjective. “This codebase is messy” becomes “maintainability score is 68, here are the top five categories of issues.”
That visibility is useful for prioritization. You can focus on the files or modules with the worst scores rather than guessing where the problems are.
But scores create pressure. Once quality becomes measurable, it becomes something teams get judged on. That can drive better code or it can drive gaming the metrics. It depends on the culture.
What this says about GitHub’s strategy#
GitHub is integrating AI-assisted quality checks, AI-powered code review, and now AI-driven quality improvements. The pattern is clear: they’re building toward a full AI development workflow where code gets generated, reviewed, tested, and quality-checked with AI assistance at every step.
Code Quality is another piece of that. It closes the loop between “Copilot writes code” and “Copilot ensures that code meets quality standards.”
The question is whether that’s the workflow developers actually want, or whether there’s a point where too much automation makes you lose touch with your codebase.
Bottom line#
GitHub Code Quality is free during preview (but scans use Actions minutes), and it’s available for GitHub Enterprise Cloud and Team customers. If you’re already using CodeQL for security, adding quality checks is a small step.
The real value is whether having quality feedback in-context during pull requests changes team behavior. If it does — if teams start treating maintainability issues as seriously as functional bugs — then this becomes a meaningful shift.
If it just creates more notifications that developers learn to ignore, then it’s another tool that lives in the backlog.
Learn more: Check the GitHub Code Quality documentation for setup instructions and available quality rules.